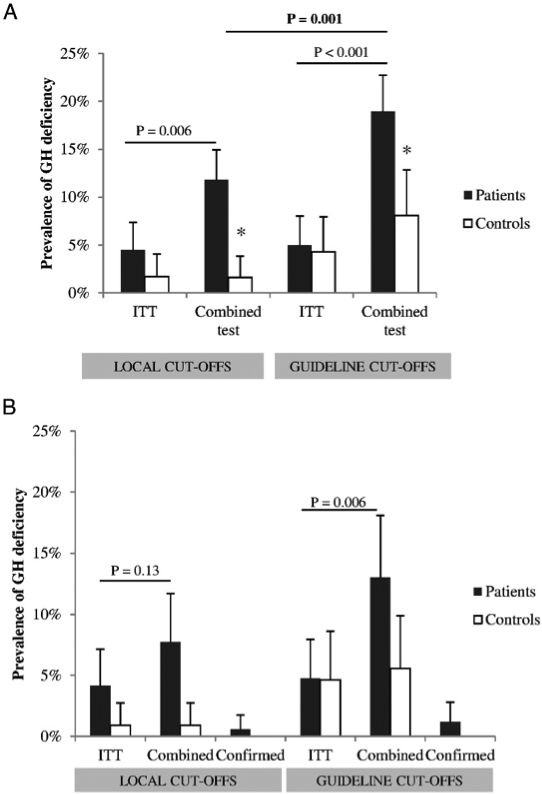
Figure 12. The prevalence of insufficient test responses in the total cohort (A) and in the subgroup undergoing dual testing (B). A, Prevalence of insufficient test responses to either ITT or PD-GHRH/GHRH-Argo (i.e., combined tests) in the total cohort of TBI patients (black columns) and healthy controls (white columns), respectively, as defined by either local or guideline-derived cut-offs. Whiskers indicate the 95% CI. GHD was more frequently diagnosed in TBI patients tested by a combined test as compared with ITT, and even more so if guideline cut-off values were applied instead of local cut-offs. The results from healthy controls illustrate the high false-positive rate resulting from application of guideline-derived cut-offs, which was significantly above the generally accepted 2.5% for the combined tests (P = .02). *, P < .005 compared with patients. B, Prevalence of insufficient test responses in the subgroups of patients (black columns, n = 169) and controls (white columns, n = 117) undergoing dual testing, as defined by either local cut-off values or guideline-derived cut-off values. Confirmed insufficiency was defined as a concordant positive result to both the ITT and a combined test. Whiskers indicate the 95% CI. [Reproduced with permission]. From: Klose et al. (119).
