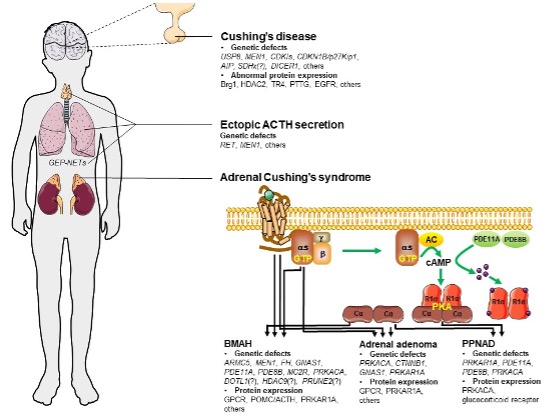
Figure 5. Genetic defects of Cushing’s disease and Cushing’s syndrome. AC: adenylate cyclase; ACTH:
adrenocorticotropic hormone; AIP: aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-interacting protein; ARMC5: armadillo
repeat containing 5; BMAH: bilateral macronodular adrenal hyperplasia; Brg1: Brahma-related gene 1;
Cα: catalytic subunit of PKA; CDKI: cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor; CDKN1B (also known as
p27Kip1); CTNNB1: catenin beta 1; DOT1: Disruptor of telomeric silencing 1; EGFR: epidermal growth
factor receptor; GNAS: Guanine Nucleotide binding protein; GPCR: G-protein-coupled receptor; HDAC2:
Histone Deacetylase 2; MC2R: melanocortin 2 receptor; MEN1: multiple endocrine neoplasia 1; PDEs:
phosphodiesterases; PKA: protein kinase A; POMC: Pro-opiomelanocortin; PPNAD: primary pigmented
nodular adrenocortical disease; PRUNE2: prune homologue 2; PTTG: pituitary transforming gene; Rlα:
type 1α regulatory subunit of PKA; SDH: succinate dehydrogenase subunit; TR4: testicular orphan
receptor 4; USP8: ubiquitin-specific peptidase 8.
