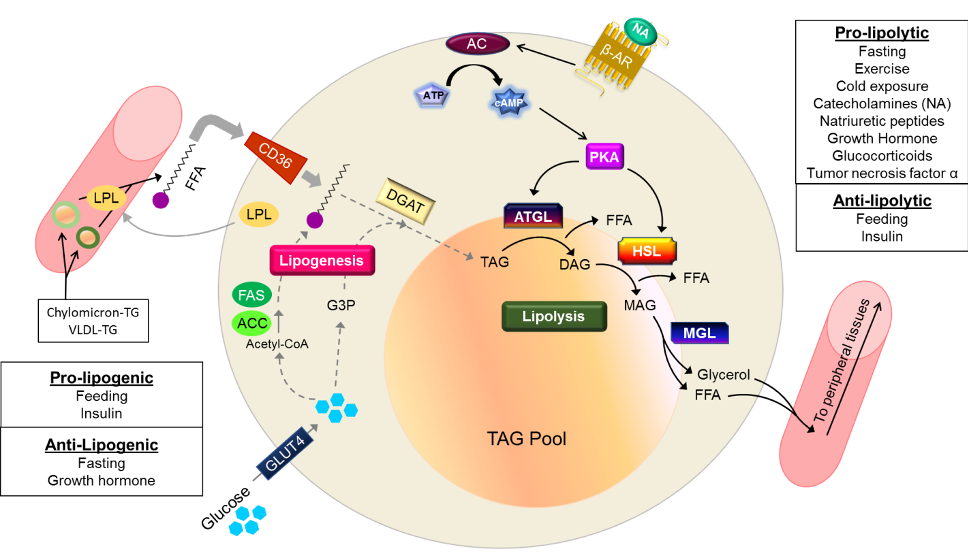
Figure 4. A critical balance between lipogenesis and lipolysis within adipocytes must be established to maintain whole body insulin sensitivity and energy homeostasis. Lipogenesis is shown on the left (gray arrows mark the pathway), whereas lipolysis is shown on the right and is marked by black arrows. Nutritional and hormonal cues regulate both processes. Lipid droplet associated proteins, such as perilipin and comparative gene identification-58 (CGI-58) are not shown but play important roles in lipolysis. CD36 (cluster of differentiation 36) is a fatty acid transporter that facilitates entry of free fatty acids (FFAs) into the cell. Insulin stimulates glucose uptake into fat cells by increasing the localization of the insulin responsive glucose transporter, GLUT4, within the plasma membrane. Other abbreviations: VLDL-TG – triglyceride-containing very low density lipoprotein; LPL – lipoprotein lipase; ACC – acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; FAS – fatty acid synthase; G3P – glycerol 3 phosphate; DGAT – diacylglycerol acyltransferase; β-AR – β-adrenergic receptor; NA – noradrenaline; AC – adenylyl cyclase; PKA – protein kinase A; ATGL – adipocyte triglyceride lipase; HSL – hormone sensitive lipase; MGL – monoacylglycerol lipase; TAG – triacylglycerol; DAG – diacylglycerol; MAG – monoacylglycerol.
