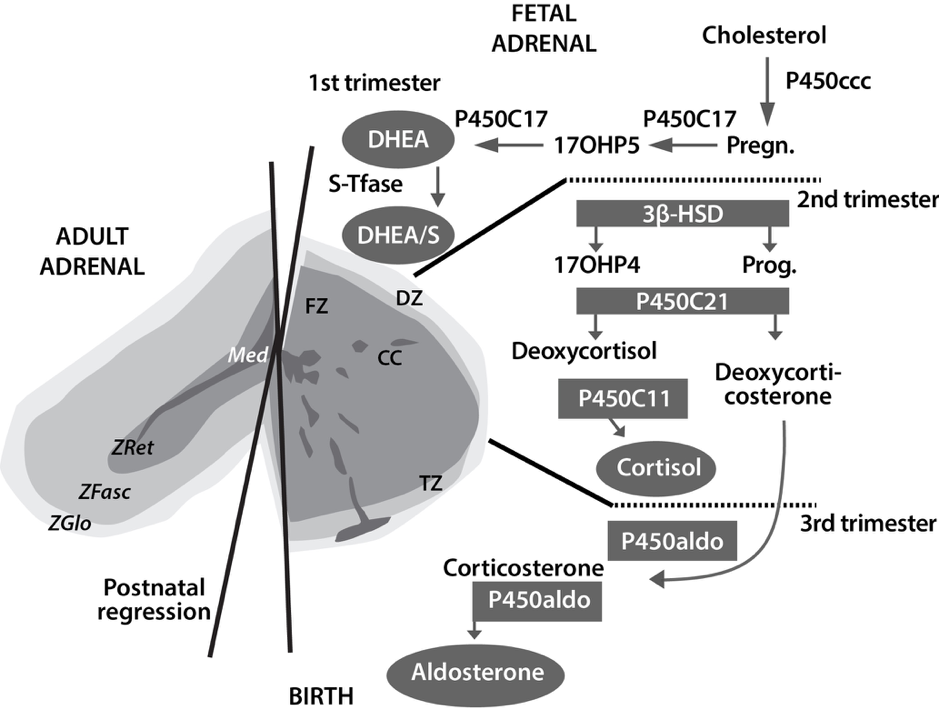
Figure 1: Ontogenesis of steroidogenic enzymes in the human fetal adrenal gland. This schematic representation is divided into portions showing the fetal adrenal gland (right) at the first, second and third trimesters of pregnancy, and the adult adrenal gland (left). During the first trimester, the fetal gland is composed of a definitive zone (DZ, light grey) and a fetal zone (FZ, darker grey). Fetal zone (FZ) – expressing the P450C17 cytochrome, is responsible for massive secretion of DHEA and DHEA/S, used by the placenta as estrogen precursors. Second trimester – chromaffin cells (CC, darkest grey) originating from the neural crests migrate through the fetal cortex to progressively colonize the center of the gland to form the future medulla (Med). Third trimester – the newly constituted transitional zone (TZ, medium grey) acquires the enzyme 3ß-HSD while the expression of P450C17 remains, thus allowing the production of fetal cortisol. Near birth, cells of the definitive zone which express only 3ß-HSD, acquire the P450aldo and begin to secrete mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone. Neonatal – the fetal adrenal regresses strongly (mainly due to the regression of the fetal zone) and recovers progressively during the first years of extra-uterine life. Adult – adult adrenal gland is composed of the zona glomerulosa (ZGlo, light grey), zona fasciculata (ZFasc, medium grey) and zona reticularis (ZRet, darker grey) responsible for the production of mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), glucocorticoids (cortisol) and androgens (DHEA-DHEA/S), respectively. P450scc – cytochrome P450 side chain cleavage; Pregn. – pregnenolone; P450C17 – cytochrome P450 17a-hydroxylase, 17-20 lyase; 17OHP5 – 17-hydroxy-pregnenolone; DHEA/S – dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate; S-Tfase – DHEA sulfotransferase; 3ß-HSD – 3ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; Prog. – progesterone; 17OHP4 – 17-hydroxyprogesterone; P450C21 – cytochrome P450 21-hydroxylase; P450C11 – cytochrome P450 11ß-hydroxylase; P450aldo – cytochrome P450 aldosterone synthase.
