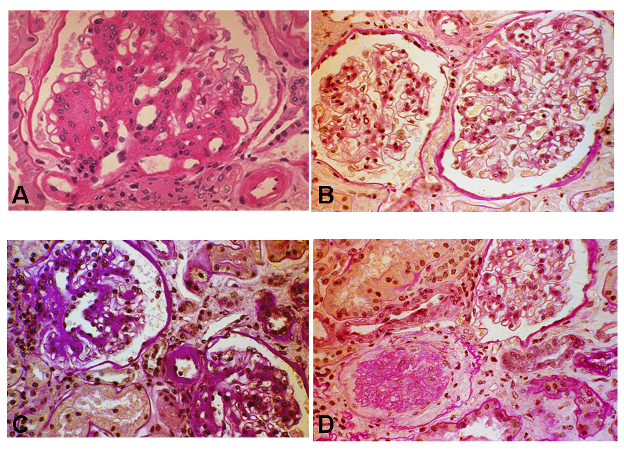
Figure 5. Light microscopy photographs of glomeruli of patients with type 1 (A) and type 2 diabetes (B-D). A. Diffuse and nodular mesangial expansion and arteriolar hyalinosis in this glomerulus from a microalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patient [Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) X 400]. B. Normal or near normal renal structure in this glomerulus from a microalbuminuric type 2 diabetic patient (PAS X 400). This photograph was kindly provided by Dr. Paola Fioretto. C. Changes “typical” of diabetic nephropathology (glomerular, tubulo-interstitial and arteriolar changes occurring in parallel) in this renal biopsy from a microalbuminuric type 2 diabetic patient (PAS X 400). D. “Atypical” patterns of injury, with absent or only mild diabetic glomerular changes associated with disproportionately severe tubulo-interstitial changes. Note also a glomerulus undergoing glomerular sclerosis (PAS X 400). Source: Reprinted with permission from National Kidney Foundation. Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Diabetic Nephropathy. Caramori ML, Mauer M. Primer on Kidney Diseases, 5th Edition, Greenberg A, et al., Copyright 2009 (253).
