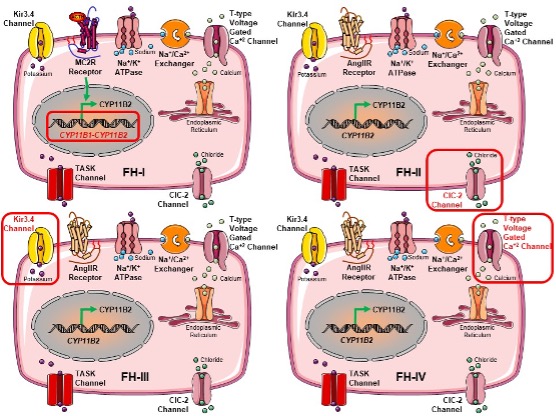
Figure 2. Genetic defects of the types of Familial Hyperaldosteronism (FH). FH-I is caused by the fusion of CYP11B1 encoding for 11β-hydroxylase, and the CYP11B2 that expresses aldosterone synthase. The molecular basis of FH-II has been attributed to activating mutations in the CLCN2 encoding for the chloride channel 2. FH-III is caused by germline activating mutations in the KCNJ5 that expresses the potassium channel GIRK4 (Kir3.4). FH-IV has been associated with mutations in the CACNA1H that encodes for the alpha subunit of the voltage-dependent T-type calcium channel Cav3.2.
