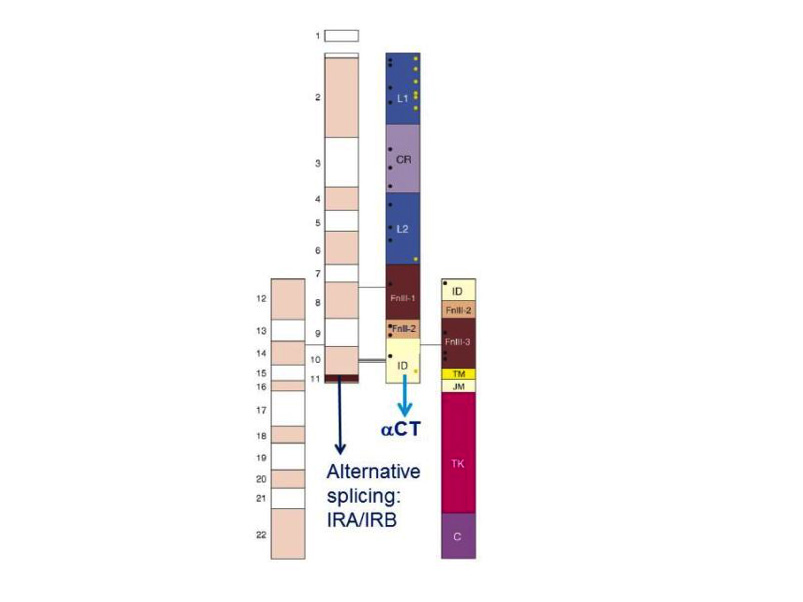
Figure 3. Modular structure of the insulin receptor. Cartoon of the α2β2 structure of the insulin receptor, drawn to scale. On the left half of the receptor, spans of the 22 exon-encoded sequences. On the right half, spans of predicted protein modules. Module boundaries mostly correspond to exon boundaries. L1 and L2: Large domains 1 and 2 (leucine-rich repeats); CR: Cys-rich domain. FnIII-1, FnIII-2, FnIII-3: Fibronectin III domains. ID: insert in FnIII-2. TM: transmembrane domain. JM: juxtamembrane domain. TK: tyrosine kinase domain. C: C-terminal tail. Black rectangle near FnIII-1: major immunogenic region. Orange dots: N-glycosylation sites. Black dots: ligand binding ”hotspots” identified by single amino acids site-directed mutagenesis. The two α-subunits are linked by a disulfide bond between the two Cys 524 in the first FnIII domain. One to three of the triplet Cys at 682, 683 and 685 in the insert within the second FnIII domain are also involved in α-α disulfide bridges. There is a single disulfide bridge between α and β subunits between Cys 647 in the insert domain and Cys 872 (nomenclature of the B isoform) . Exon 11 is highlighted. Adapted from reference 25.