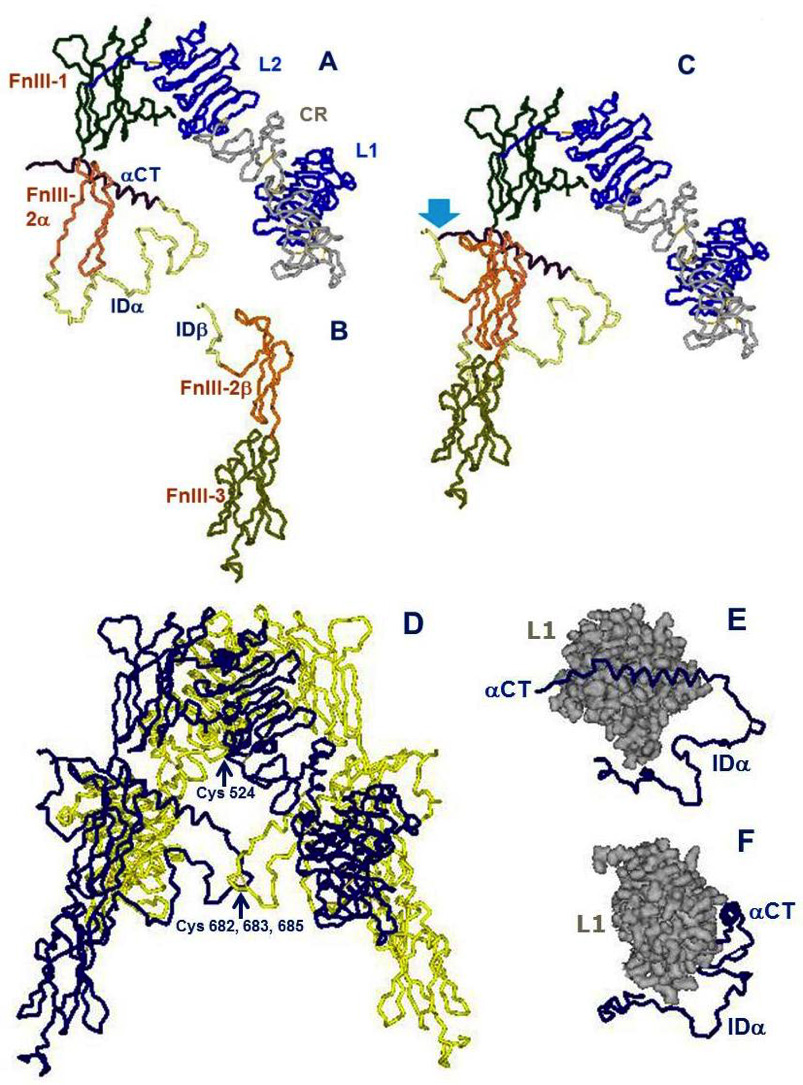
Figure 4. Architectural assembly of the unbound insulin receptor ectodomain. This figure is based on the latest higher resolution structure of the apo-receptor at 3.3 Å resolution (38). A. The α subunit. Domains are labeled as in Figure 3. FnIII-2α is the α subunit component of the FnIII-2 domain. B. The β subunit. Domains are labeled as in Figure 3. FnIII-2β is the β subunit component of the FnIII-2 domain. C. The αβ monomer. The monomer shows an inverted V-shaped structure. The arrow denotes the site of proteolytic cleavage of the proreceptor. This structure is the A-isoform of the insulin receptor. Twelve amino acids at the end of the insert domain of the β subunit are missing from the structure. The B-isoform would have 12 more amino acids encoded by exon 11 at the end of the αCT domain of the α subunit..D. The α2β2 dimer. The arrow indicates the location of the triplet of disulfide bonds between Cys 682, 683 and 685 of the two α subunits. E. The tandem insulin binding site 1 made of the αCT helical segment of one α subunit binding in trans to the beta sheet surface of the L1 domain of the second α subunit. The rest of the α subunit insert (ID), which is not part of the binding site, is also shown for orientation. F. Idem, rotated 90 degrees. Drawn using DSViewerPro from PDB file Model-S1 2, kindly provided by Mike Lawrence, based on PDB file 4ZXB complemented using IMDFF (38).